German researchers led by Dr. Neetesh Singh and Professor Franz Keltner have developed a high-power tunable laser based on silicon photonics. In this work, they used a large-mode-area integrated waveguide amplifier (LMA) to achieve an output power of about 2 watts. The work was published in the journal Light: Science & Applications .
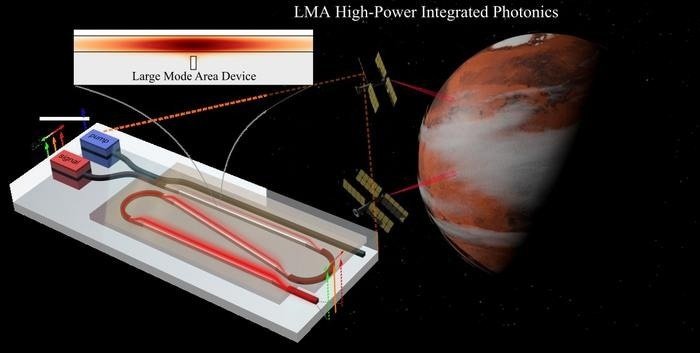
In the modern world, the systems that support increasingly smaller components are becoming smaller and smaller. Examples of these systems include high-speed data centers and the small satellites used for space exploration.
However, the signal power generation capability of such systems is significantly reduced due to the miniaturization and high-density integration achieved by integrated photonics.High-power systems have traditionally been considered in meter-scale systems such as fiber optics and solid-state systems, as their large capacity allows for large-capacity energy storage.
The power generation capacity of integrated photonic systems is still much lower than that of bench-top systems because the light energy storage capacity is much smaller in micrometer- to millimeter-scale systems such as integrated photonics-based systems.
Silicon photonics-based lasers and amplifiers need to generate high-power signals at levels comparable to benchtop systems to enable large-scale deployment of capable, mass-producible silicon photonics systems to replace bulky benchtop systems.
According to the researchers, such a device could revolutionize the field of photonics, enabling the widespread use of integrated photonic devices in various applications.
One potential application is to put high-power tunable lasers with long wavelength windows on small satellites to detect and map (using techniques such as LIDAR) molecules essential for life in space, such as carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia.
Compared to traditional fiber-based or solid-state systems, high-power tunable lasers based on silicon photonics LMAs reduce system size, weight, and cost by several orders of magnitude, enabling many affordable space missions with significantly enhanced capabilities that were previously unattainable.
This research is supported by the EU Framework Programme “Horizon 2020” and the German Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SP2111) programme.
Journal References:
Singh, N., et al . (2025) Sub-2W tunable laser based on silicon photonic power amplifier. Photonic Science and Applications . doi.org/10.1038/s41377-024-01681-1.
sauce:
Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences